How Do You Stimulate Cell Regeneration?
The human body is a remarkable self-repairing system. Every day, cells throughout your body regenerate to replace old, damaged, or dying ones. This cell regeneration process is critical for tissue repair, overall health, and even slowing the effects of aging. Understanding how to stimulate cell regeneration can empower you to take proactive steps to support your body’s natural healing processes. Whether through diet, lifestyle, or advanced therapies, there are many effective ways to encourage cell renewal and maintain optimal health. In this blog, we’ll explore the science behind cell regeneration, the key factors that influence it, and practical methods to stimulate this process.
Understanding Cell Regeneration
Cell regeneration refers to the body’s ability to produce new cells to replace damaged or dead ones. It occurs naturally as part of the cellular life cycle, which involves:
Cell Division
Healthy cells divide to form new ones, ensuring the body constantly supplies functional cells to maintain essential processes and overall health.
Repair and Replacement
Fresh, functional cells replace damaged or dying cells, allowing tissues and organs to maintain their proper structure and performance.
Tissue Regeneration
New cells contribute to tissue repair, restoring strength, flexibility, and functionality to areas affected by damage or wear.
The rate of regeneration depends on the type of tissue. For example:
Skin Cell Regeneration
Skin cells regenerate quickly, with the outer layer renewing itself approximately every 28 days, keeping the skin healthy, protective, and resilient.
Liver Cell Regeneration
Liver cells can regenerate relatively fast, allowing the liver to recover from injury or partial removal while continuing its critical detoxification functions.
Nerve Cell Regeneration
Nerve cells regenerate very slowly or not in certain cases, although emerging research offers hope for enhanced nerve repair and recovery.
Factors That Influence Cell Regeneration
Several factors affect the body’s ability to regenerate cells. These include:
Nutrition
Nutrients play a critical role in cell regeneration. A diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants provides the building blocks necessary for healthy cells.
Lifestyle Habits
Exercise, sleep, and stress management all impact the body’s regenerative capacity. A healthy lifestyle supports optimal cell function and repair.
Age
As we age, cellular processes slow down. While this is natural, the effects of aging can be mitigated with proper care.
Environmental Factors
Toxins, pollutants, and UV radiation can damage cells and inhibit regeneration. Minimizing exposure to harmful elements is essential for maintaining cell health.
Medical Conditions
Certain chronic conditions, such as diabetes, autoimmune diseases, or circulatory problems, can impair the body’s ability to repair itself. Managing these conditions can help restore regenerative function.
Eight Ways to Stimulate Cell Regeneration Naturally
Discover simple and effective ways to support your body’s natural ability to repair and renew itself. From mindful nutrition and hydration to sleep, exercise, and stress management, learn how small lifestyle changes can enhance cell regeneration for improved health and vitality.

1. Optimize Your Diet
Nutrition is the foundation for healthy cell regeneration. Focus on incorporating the following nutrients into your diet:
Protein
Amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, are essential for cell repair and tissue regeneration. Include lean meats, fish, eggs, legumes, and plant-based protein sources.
Vitamins A, C, and E
These antioxidants protect cells from damage while promoting regeneration. Foods like citrus fruits, carrots, leafy greens, and nuts are excellent sources.
Zinc
Zinc is crucial for cell division and repair. Add foods like pumpkin seeds, lentils, and shellfish to your meals.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, omega-3s reduce inflammation and support cell membrane integrity.
Collagen
Collagen-rich foods like bone broth help repair tissues, especially skin and connective tissues.
Antioxidants
Berries, green tea, and dark chocolate are rich in antioxidants, neutralizing free radicals that damage cells.
2. Stay Hydrated
Water is essential for every cell in the body. Proper hydration helps transport nutrients to cells, remove toxins, and support overall cellular function. Aim for at least eight glasses of water a day, adjusting based on your activity level and environment.
3. Engage in Regular Exercise
Physical activity stimulates blood flow, delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues, which enhances cell regeneration. Regular exercise also promotes the production of growth factors and stem cells, which are key players in repair processes.
Aerobic Exercise
Activities like walking, running, or cycling improve circulation and oxygenate tissues.
Strength Training
Weightlifting and resistance exercises stimulate muscle repair and growth.
Stretching and Flexibility
Yoga and Pilates encourage cellular renewal by improving blood flow to tissues.
4. Prioritize Quality Sleep
Sleep is critical for cell regeneration. During deep sleep, the body releases growth hormones, which stimulate tissue repair and cellular renewal.
High-Quality Sleep
Consistent, high-quality sleep allows your body to repair damaged cells.
Establish a Routine
Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day supports your body’s natural rhythms.
Optimize Your Sleep Environment
Keep your room cool, dark, and quiet to promote restful sleep.
5. Reduce Stress
Chronic stress produces cortisol, which can impair cellular repair and regeneration. Effectively managing stress is crucial for supporting healthy cells.
Practice Mindfulness
Techniques like meditation and deep breathing can reduce stress levels.
Engage in Relaxing Activities
Hobbies, time in nature, or gentle movements like tai chi can calm the mind and body.
Maintain Work-Life Balance
Prioritize downtime to allow your body and mind to recharge.
6. Protect Your Skin and Tissues
The skin is the body’s largest organ and a visible indicator of cell regeneration. Protecting your skin helps promote renewal and prevents damage.
Use Sunscreen
UV radiation accelerates cell damage and aging. Apply a broad-spectrum SPF daily.
Moisturize
Hydrated skin regenerates more efficiently.
Avoid Smoking and Excess Alcohol
Both habits inhibit cell regeneration and accelerate aging.
7. Support Gut Health
A healthy gut plays a critical role in cell regeneration. Your gut microbiome influences immune function, nutrient absorption, and inflammation levels.
Eat Probiotic Foods
Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi support healthy gut bacteria.
Consume Prebiotics
Foods like garlic, onions, and bananas feed beneficial bacteria.
Avoid Processed Foods
Reducing sugar and processed food intake minimizes inflammation, which can slow cellular repair.
8. Incorporate Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting can stimulate a process called autophagy, where the body removes damaged cells and generates new, healthy ones. Fasting allows the body to focus on repair rather than digestion.
Start With a 12-16 Hour Fasting Window
Begin with a manageable fasting period, such as 12 to 16 hours, to allow the body to enter a repair-focused state. Gradually increase the duration if desired and monitor how your body responds.
Focus on Nutrient-Dense Foods
During eating periods, prioritize foods rich in vitamins, antioxidants, and proteins to give your body the essential nutrients it needs to build and regenerate healthy cells. Avoid processed and sugary foods that can negate the benefits of fasting.
Advanced Methods for Stimulating Cell Regeneration
In addition to natural strategies, medical advancements offer therapies to boost cell regeneration for specific needs.
Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can become various types of specialized cells. Stem cell therapy involves using these cells to repair tissues and regenerate damaged areas. This therapy is especially promising for nerve damage, joint injuries, and chronic wounds.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy uses the patient’s blood, which is processed to concentrate platelets rich in growth factors. When injected into an injury site, PRP stimulates healing, promotes tissue repair, and encourages cell regeneration.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized environment. The increased oxygen levels boost blood flow, reduce inflammation, and accelerate cellular repair, particularly in chronic wounds or injuries.
Red Light Therapy
Red light therapy uses low-level wavelengths of light to stimulate mitochondrial activity in cells, promoting regeneration. This therapy is often used for skin repair, reducing inflammation, and supporting tissue recovery.
Peptide Therapy
Peptides are short chains of amino acids that act as signaling molecules in the body. Certain peptides, such as BPC-157 or TB-500, have shown promise in accelerating tissue repair and reducing inflammation.
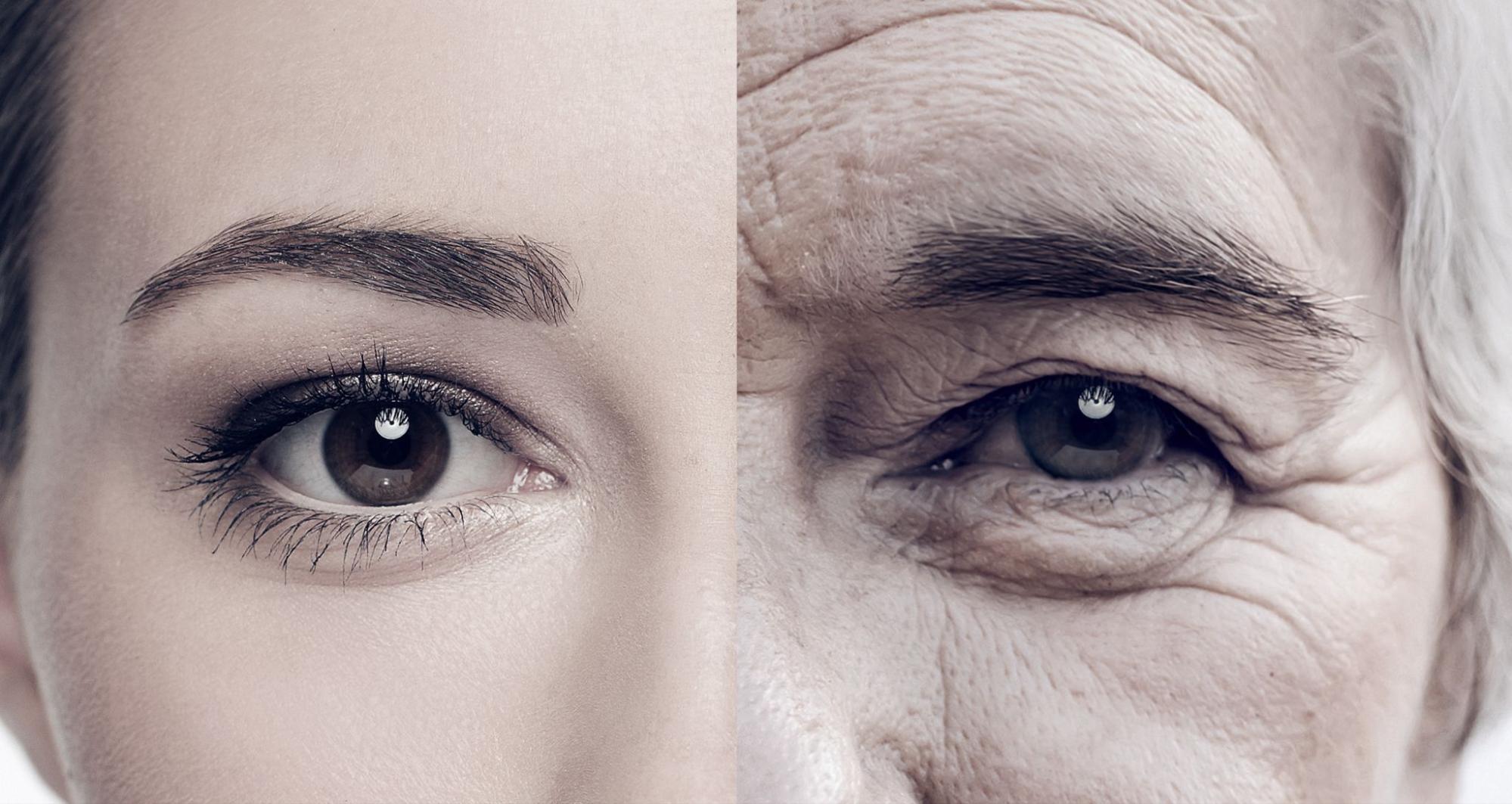

The Role of Cell Regeneration in Aging and Health
Cell regeneration is vital for healing injuries, significantly slows the aging process, and maintains overall health. As cellular repair declines with age, prioritizing regenerative strategies can help:
Improve Skin Elasticity and Reduce Wrinkles
By stimulating collagen production and increasing cell turnover, you can maintain smoother, firmer skin and reduce visible signs of aging.
Support Joint Health and Mobility
Regenerating cartilage and connective tissue helps reduce stiffness and inflammation, improving joint flexibility and overall mobility.
Enhance Energy Levels and Cognitive Function
Improved cellular repair supports mitochondrial function, which increases energy production and enhances brain health, memory, and focus.
Strengthen the Immune System
Healthy cell regeneration bolsters immune function, enabling the body to fight infections and recover more efficiently from illness or injury.
Stimulate Cell Regeneration for Health and Longevity
Stimulating cell regeneration is essential for overall health and longevity. By optimizing your diet, prioritizing sleep, managing stress, and incorporating regular exercise, you can naturally enhance your body’s ability to repair and regenerate cells. Advanced therapies like stem cell treatment and PRP offer additional support for those facing specific challenges. Taking proactive steps to stimulate cell regeneration promotes healing and helps slow the effects of aging, allowing you to enjoy a healthier and more vibrant life. Start today by making small changes that support your body’s incredible ability to renew itself.
Discover more strategies to support cell regeneration and overall vitality by exploring the Stem Health Plus LLC blog for expert insights and tips.
