
Preventing Wound Infection: Essential Tips for Proper Wound Care
Wounds are common in life, whether caused by a minor cut, scrape, burn, or more severe injury. While most wounds heal naturally with minimal intervention, improper wound care can lead to infections, which can complicate the healing process and, in some cases, lead to more serious complications. Understanding the essential steps in wound care is critical to preventing infection and promoting optimal healing. This blog will explore the importance of proper wound care, critical tips to prevent infection, and steps to take if an infection occurs.
Why Wound Care is Important for Preventing Infection
When a wound occurs, the skin’s protective barrier is disrupted, making the body vulnerable to infection by bacteria, fungi, or viruses. An untreated or improperly treated wound can easily become infected, leading to inflammation, pain, and pus formation. Occasionally, untreated infections can spread to deeper tissues or even enter the bloodstream, leading to sepsis—a potentially life-threatening condition. Proper wound care is essential to minimize the risk of infection and ensure faster healing. It involves cleaning the wound, applying appropriate dressings, and following safety precautions to protect it from contaminants.
Step-By-Step Guide to Proper Wound Care
To minimize the risk of infection and promote optimal healing, follow these essential steps for proper wound care:
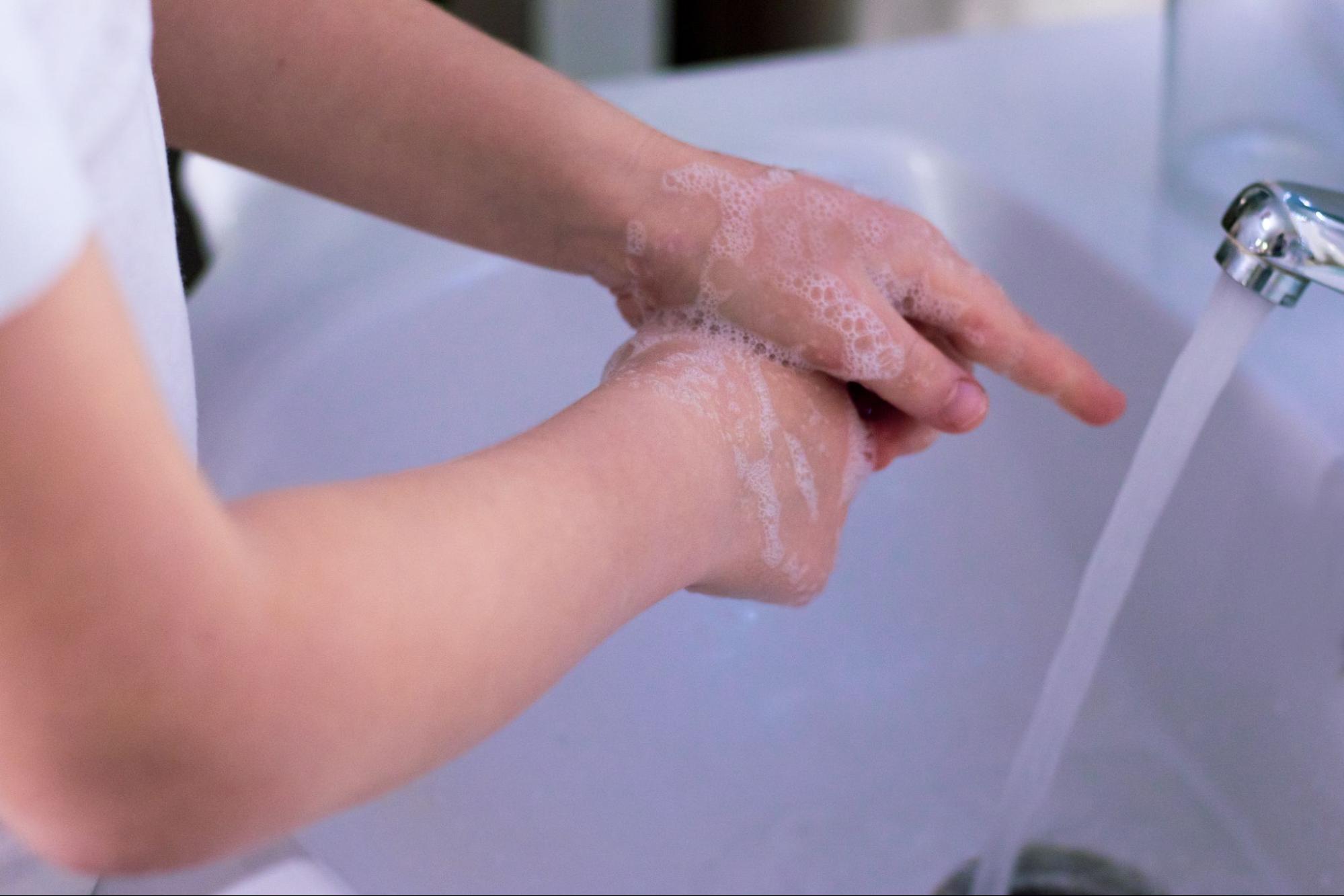
1. Wash Your Hands Thoroughly
Before handling any wound, the first and most important step is to wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water. This step reduces the risk of transferring harmful bacteria to the wound site. Make sure to scrub all areas of your hands, including your fingers, nails, and wrists, for at least 20 seconds. If soap and water are not available, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol.
2. Clean the Wound Gently
The next step is to clean the wound. Start by gently rinsing the wound with clean, lukewarm water. Avoid using hydrogen peroxide or alcohol to clean the wound, as these can damage healthy tissue and slow down the healing process. Instead, use mild soap and water if necessary. If the wound is large or deeply punctured or if it is heavily contaminated (e.g., from dirt or gravel), you may need to irrigate it with a sterile saline solution. You can buy saline solution from a pharmacy or make a simple saline solution at home by mixing one teaspoon of salt with 1 cup of warm water.
3. Remove Debris and Foreign Objects
If foreign objects or debris, such as glass, dirt, or clothing fibers, are in the wound, it is essential to remove them. You can do this carefully with sterilized tweezers. Seek medical attention if the object is embedded deeply in the wound or cannot be removed easily. Do not attempt to remove deeply embedded objects yourself, as doing so may cause more damage.
4. Apply an Antiseptic
Once the wound is clean, apply a gentle antiseptic solution to kill any remaining bacteria. Choose an antiseptic that is safe for wounds, such as iodine-based solutions or antiseptic ointments, like Neosporin or Bacitracin. Avoid using products with alcohol or hydrogen peroxide directly on the wound, as these can irritate the tissue and delay healing.
5. Dry the Wound
After cleaning and applying antiseptic, gently pat the wound dry with a clean, sterile gauze or towel. Avoid rubbing the wound, as this can cause further irritation.
6. Dress the Wound
Covering the wound with a clean, sterile dressing or bandage helps protect it from external contaminants and keeps the area moist, which promotes faster healing. Use an appropriate dressing for the type of wound. Adhesive bandages may suffice for minor cuts and scrapes, while gauze pads and medical tape may be required for more significant wounds or surgical sites. Use absorbent dressings like hydrocolloid or alginate dressings for wounds that produce a lot of drainage. Always change the dressing regularly to ensure it remains clean and dry. Change the bandage as soon as it becomes wet or dirty, as this can increase the risk of infection.
7. Keep the Wound Clean and Dry
Once the wound is covered, try to keep it clean and dry. This step means avoiding excessive moisture, such as water, which can introduce bacteria into the wound. If the wound is in a high-moisture area (such as the hands or feet), you may want to use a waterproof bandage or dressing to protect it during washing or bathing. Avoid exposing the wound to excessive dirt, and refrain from rubbing or scratching the wound area, as this can lead to irritation and may introduce harmful bacteria.

Tips for Preventing Wound Infection
Proper wound care is essential for preventing infection, but you can also implement other strategies to reduce the risk. Here are some additional tips:
1. Use Sterile or Clean Materials
Always use sterile or clean materials when cleaning, dressing, or changing your wound bandages, such as freshly opened bandages, gauze pads, and sterile tweezers or scissors. Reusing non-sterile materials can introduce harmful bacteria into the wound and lead to infection.
2. Watch for Signs of Infection
Even with proper care, there is always the possibility of an infection developing. Be on the lookout for signs of infection, which include:
Redness and Warmth Around the Wound
One of the earliest signs of infection is the development of redness and warmth around the wound. This sign occurs as the body responds to the injury, increasing blood flow to the area to fight off potential bacteria. If the redness and warmth persist or expand, it may indicate that the wound is infected.
Increased Swelling or Pain
Increased swelling or pain around the wound can indicate infection or an inflammatory response. Swelling may suggest that the body sends more white blood cells to fight the infection, while pain often results from
inflamed or irritated tissue. If swelling and pain worsen, it’s crucial to seek medical attention.
Pus or Discharge From the Wound
Pus or other types of discharge coming from the wound are common indicators of infection. This fluid is a mixture of dead cells, bacteria, and immune cells fighting the infection. A change in the color, consistency, or amount of discharge can signal that the infection is progressing and needs medical evaluation.
Fever or Chills
Fever or chills accompanying a wound can indicate the infection has spread beyond the local area. This systemic response happens when the body raises its temperature to fight infection. If a fever develops, particularly if chills accompany it, seek medical attention, as this could indicate a more serious infection.
Foul Odor From the Wound
A foul smell from a wound is often a sign of infection, usually caused by tissue breakdown or bacterial growth. The odor can strongly indicate that the wound is not healing properly and may need medical intervention. If you notice an unpleasant odor, addressing it immediately with professional care is essential.
If you notice any of these signs, seek medical attention immediately. If left untreated, infections can spread to deeper tissues, leading to more serious health complications.
3. Keep Your Immunity Strong
A strong immune system can help your body fight off infections, including those that may develop from wounds. Eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, staying hydrated, and getting enough rest are all crucial for maintaining a healthy immune system. Suppose you have an underlying medical condition that weakens your immune system, such as diabetes or HIV. In that case, monitoring your wounds closely and consulting with a healthcare provider for additional wound care guidance is especially important.
4. Avoid Smoking
Smoking impairs circulation and slows down the body’s ability to heal wounds. It also increases the risk of developing infections. If you smoke, consider quitting, especially if you’re healing from a wound or surgical procedure.
5. Keep Tetanus Shots Up to Date
Certain types of wounds, such as those caused by rusty nails or other objects contaminated with dirt or animal feces, can put you at risk of tetanus infection. Tetanus is a serious bacterial infection that can cause muscle stiffness and, if left untreated, may lead to severe complications. Ensure your tetanus vaccinations are current, significantly if a dirty or rusty object has injured you.
6. Avoid Self-Medicating With Topical Antibiotics
While slathering on topical antibiotics like Neosporin may seem like a good idea, excessive use can lead to antibiotic resistance and irritate the skin. Use these ointments sparingly, and consult your doctor for recommendations based on your wound type.
What to Do If Preventing Wound Infection Fails
Even with the best care, wounds can sometimes become infected. If you suspect that your wound is infected, it is crucial to act quickly. Here are some steps to follow:
Promptly Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical attention immediately if you notice signs of infection such as redness, warmth, swelling, pus, or fever.
Don’t Drain the Wound
Do not attempt to drain the wound yourself. If pus or fluid is present, a healthcare provider can properly clean and drain the wound under sterile conditions.
Follow the Doctor’s Instructions
Follow your doctor’s instructions regarding wound care, especially if prescribed antibiotics or other treatments.
Monitor for Complications
Monitor for complications, such as an expanding red area or worsening pain, which may indicate the infection is spreading.
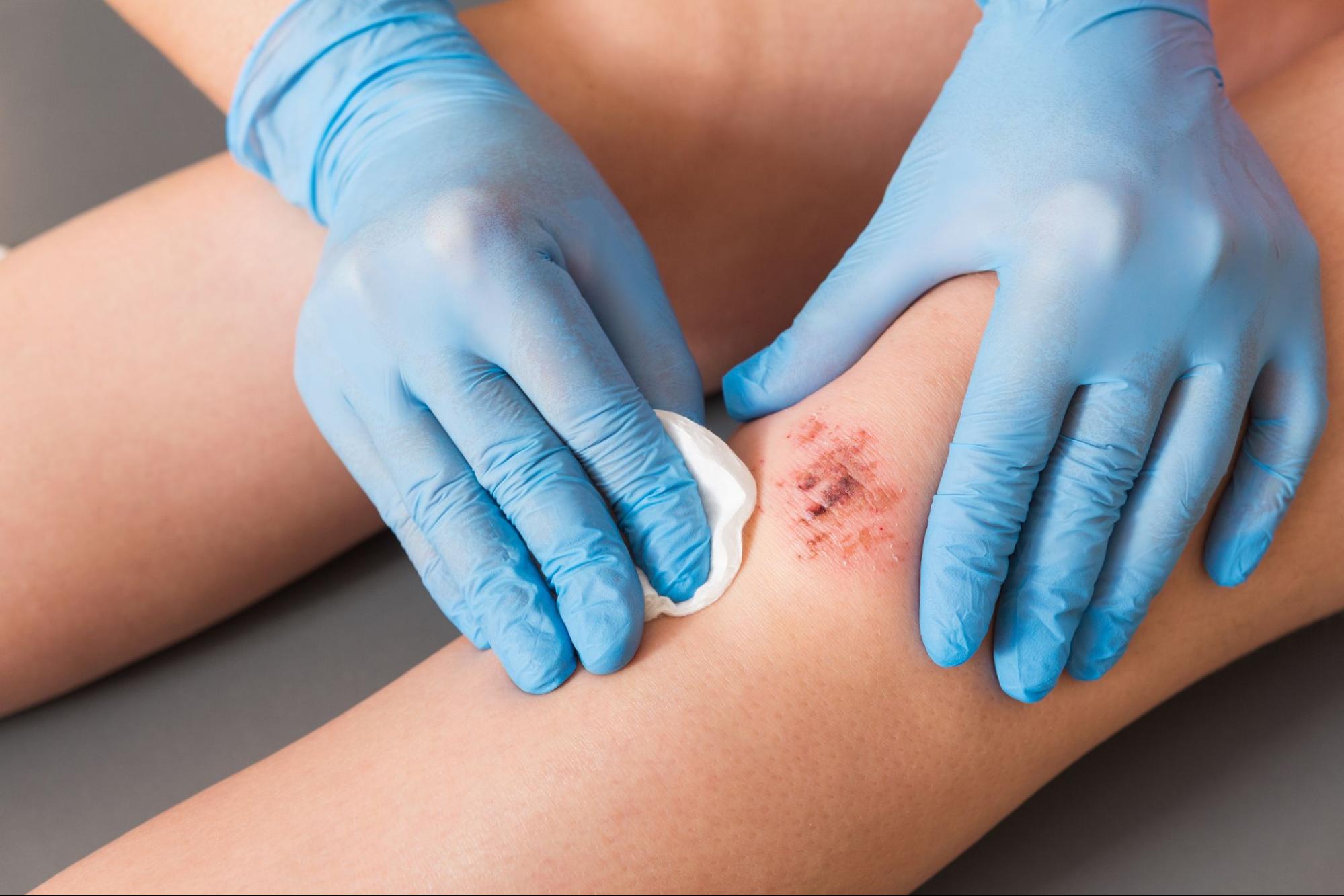
Preventing Wound Infections With Proper Wound Care
Wound infection prevention requires a combination of proper wound care techniques, awareness of infection signs, and preventive measures to keep the area clean, dry, and protected. By following these essential tips, you can reduce your risk of infection, support the healing process, and recover more quickly from injuries. If a wound shows signs of infection despite your best efforts, don’t hesitate to consult with a healthcare provider. Early intervention can prevent more serious complications and promote a faster recovery. Proper wound care isn’t just about healing the skin—it’s about safeguarding your overall health and well-being.
If you want more expert tips on maintaining your health, regenerative therapies, and preventing complications, visit the Stem Health Plus blog. From innovative therapies to general wellness advice, our blog offers valuable insights to inform and empower you on your healing journey.
