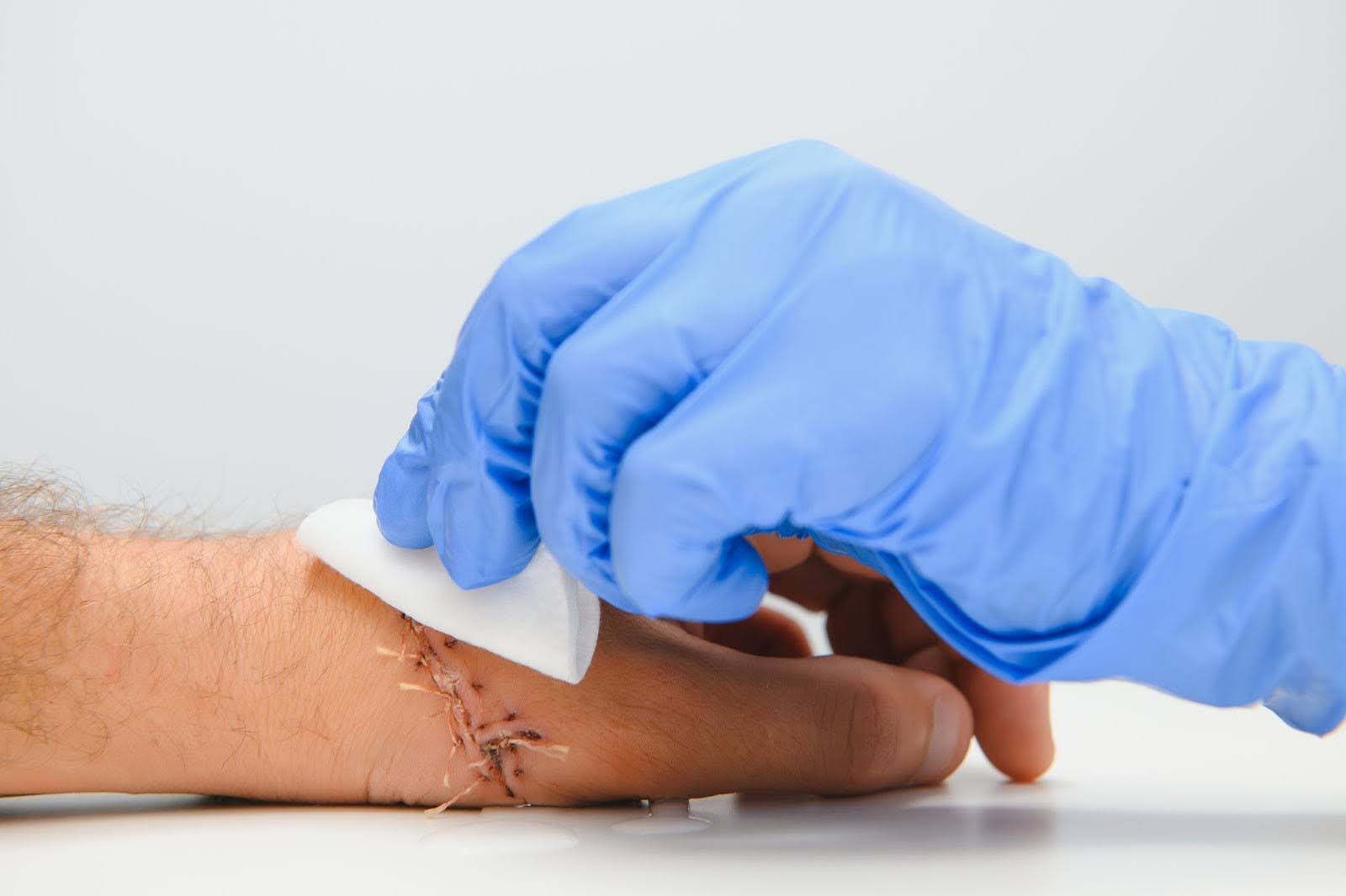
Wound Debridement: What Patients Should Expect During the Procedure
A slow-healing wound often brings discomfort, fear, and frustration. The lingering pain and uncertainty can leave patients searching for answers about why the wound won’t improve. In many cases, damaged or dead tissue prevents the body from repairing itself properly. Understanding wound debridement helps patients see that this procedure is not something to fear but a crucial step toward faster, cleaner, and safer healing.
Understanding Wound Debridement
Wound debridement is a clinical procedure that removes dead or infected tissue to promote healing and reduce infection risk. It gives the wound a clean surface where new, healthy tissue can grow. Wounds can remain stagnant and prone to further complications without removing the damaged areas. This treatment, often performed in wound care clinics, helps restart the body’s natural recovery process efficiently.
Why Dead Tissue Prevents Healing
Dead tissue, also called necrotic tissue, creates a barrier that blocks oxygen and nutrients from reaching the wound bed. This buildup traps bacteria and toxins that can lead to infection. The longer this tissue remains, the slower the body can repair itself. Removing it allows blood to circulate freely, delivering essential nutrients to the area. Doctors often describe this process as “resetting” the wound environment for proper healing.
Common Wound Debridement Techniques
Clinicians use several methods to clean and heal wounds depending on their type and condition. Surgical debridement removes dead tissue using sterile instruments for precision and speed. Mechanical debridement uses gentle friction, such as irrigation or dressing removal, to remove debris. Enzymatic debridement applies medical ointments that break down necrotic tissue chemically without damaging healthy cells. Autolytic debridement relies on the body’s moisture and enzymes to soften dead tissue naturally, while biological debridement uses sterilized maggots to remove bacteria safely.
When Debridement Becomes Necessary
Doctors recommend debridement when a wound shows no improvement after standard care or becomes infected. It is common among diabetic ulcers, pressure sores, or surgical wounds that heal poorly. Professional evaluation is essential if the wound has a dark or yellow layer, emits odor, or produces excessive drainage. Medical data from 2024 wound care reports show that regular debridement accelerates healing time by up to 40%. Patients benefit most when treatment begins once healing stalls beyond two weeks.
Preparing for a Wound Debridement Procedure
Preparation for wound debridement involves more than showing up for treatment—it ensures safety, comfort, and personalized care. Doctors perform a thorough medical assessment to understand each patient’s wound type and general health. Patients are encouraged to ask questions and share medical histories openly to help doctors choose the proper technique. This preparation minimizes complications and makes the entire experience smoother and less stressful.
Medical Assessment and Consultation
Before starting, the doctor examines the wound’s color, depth, and moisture levels to determine the proper treatment method. Diagnostic tests such as wound swabs or imaging may reveal underlying infections or tissue damage. Patients should discuss allergies, medications, and chronic conditions like diabetes or vascular disease. These details help providers plan the safest and most effective procedure. Good communication between patient and clinician builds trust and reduces anxiety about what to expect.
Comfort and Pain Control Measures
Many patients worry about pain, but modern wound care focuses on comfort. Local anesthesia or numbing creams are used for minor wounds, while mild sedation may be offered for deeper ones. The care team explains possible sensations, helping the patient stay calm and informed. Medication adjustments are discussed beforehand to avoid side effects. Clear guidance from providers helps patients feel secure and supported during the procedure.
Pre-Procedure Guidelines to Follow
Patients are often advised to eat a light meal before the appointment unless told otherwise. Loose clothing makes access to the wound area easier and more comfortable. If certain medications affect blood clotting, the doctor might recommend temporary changes. Arranging transportation home can be wise if sedation is used. Following these simple steps ensures the appointment proceeds smoothly and safely.
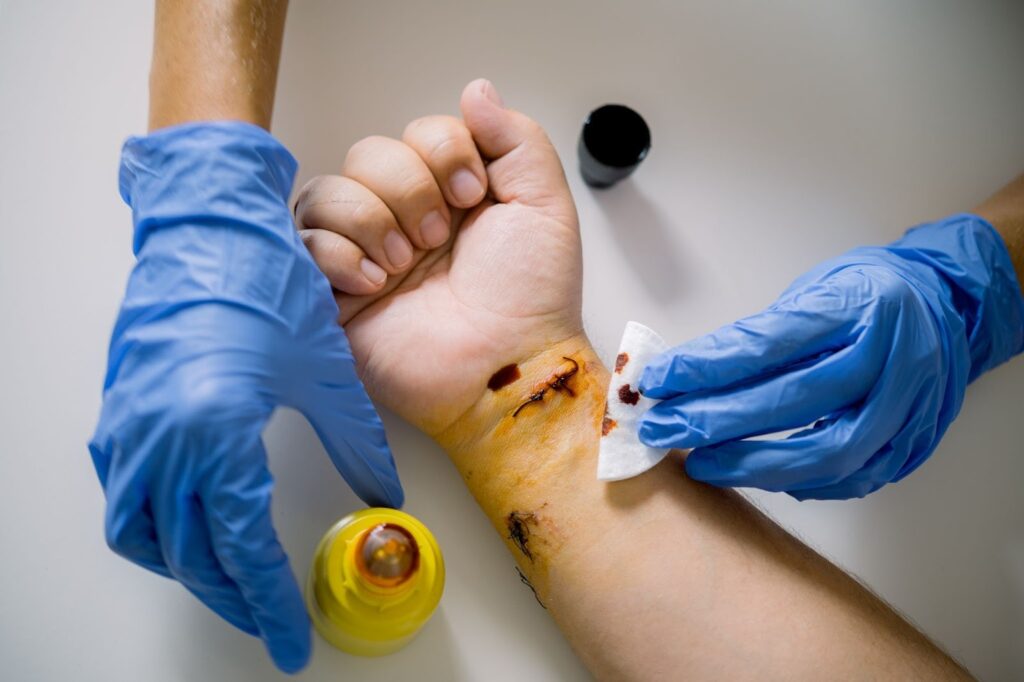
What Happens During Wound Debridement
The wound is cleaned, numbed, and carefully treated during the procedure to remove unhealthy tissue. Depending on its complexity, it may occur in a wound care clinic, outpatient center, or hospital. The doctor and nurse work together to ensure cleanliness and comfort from start to finish. Understanding each step helps patients know what to expect and reduces nervousness about the process.
Step-By-Step Debridement Process
The wound area is first cleansed with sterile saline or an antibacterial solution to reduce infection risk. Once the site is prepared, anesthesia is applied to block pain. Using the selected method, the clinician then removes necrotic tissue using surgical tools, enzymes, or moisture-based dressings. After removal, the area is irrigated again to wash away debris and checked to confirm only healthy tissue remains. A fresh, sterile dressing seals the wound to protect it during healing. Each of these steps follows strict clinical hygiene standards to prevent complications.
Duration and Frequency of Procedures
The time required varies based on wound size and the type of debridement. A small wound might take 15 minutes, while complex wounds could take up to an hour. Surgical methods are faster but sometimes require repeat sessions for complete cleaning. Autolytic or enzymatic treatments take longer since they depend on natural biological reactions. Doctors often schedule follow-up appointments to monitor progress and adjust care as needed. Healing time shortens considerably when patients maintain proper home care between visits.
The Role of the Wound Specialist
Wound care specialists receive advanced training in tissue repair and infection control. They balance precision and gentleness during every session to avoid damaging healthy tissue. Their expertise allows for quick decisions if unexpected changes appear in the wound. Nurses assist by maintaining sterile tools and monitoring the patient’s comfort throughout. This teamwork ensures the wound is treated effectively and the patient feels cared for at every stage.
Recovery and Healing After Debridement
Recovery starts immediately after the procedure and continues until the wound fully heals. Patients must follow care instructions and recognize regular changes rather than warning signs. Proper aftercare includes wound cleaning, dressing replacement, and follow-up visits to monitor progress. Maintaining good hygiene and nutrition supports faster healing and lowers infection risk.
Post-Procedure Sensations and Normal Reactions
Mild soreness or swelling is common after treatment and usually subsides within a few days. Some drainage may appear as the wound adjusts to new tissue growth. The wound might look slightly larger, but this is temporary and part of the natural healing phase. Keeping the area clean and covered helps prevent irritation or contamination. If pain worsens or the wound becomes unusually red, contacting the doctor promptly is advised.
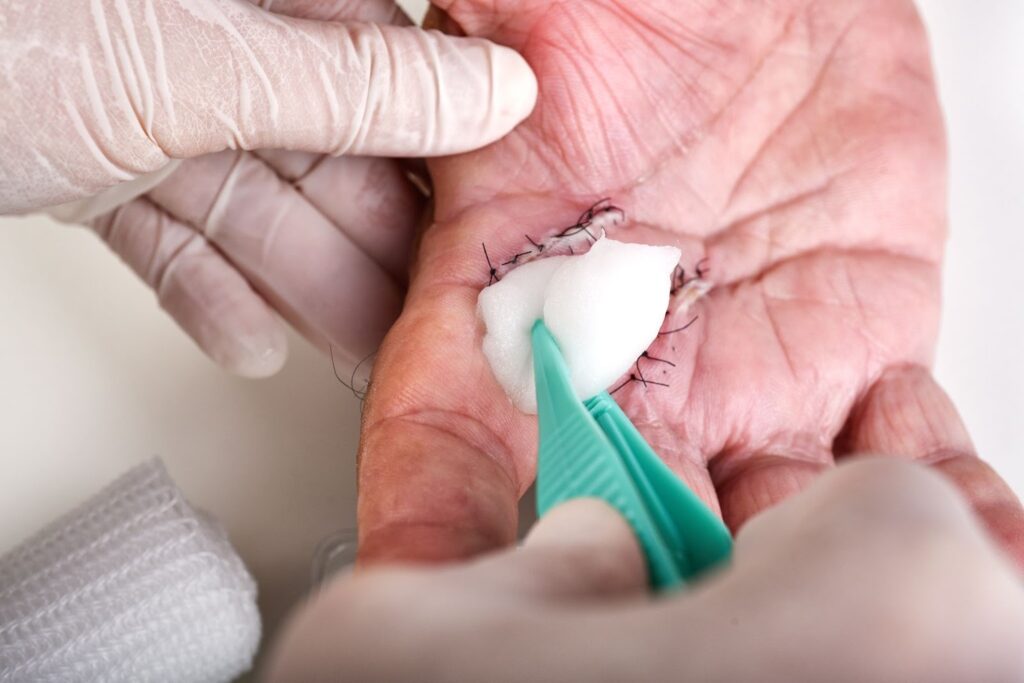
Proper Wound Cleaning and Dressing Care
The wound must remain moist but clean to allow healthy tissue to grow. Doctors typically recommend sterile saline for gentle cleaning and specific dressings suited to each wound type. Dressings should be changed as directed, often once or twice daily. Using non-stick materials prevents new tissue from tearing. Hands should always be washed before and after touching the wound. Following these simple habits can significantly improve healing speed and comfort.
Managing Pain and Medication
Pain after debridement is usually manageable with over-the-counter medication. Doctors may prescribe more substantial pain relief or antibiotics if needed. Elevating the affected area reduces swelling and improves comfort. Avoiding tight clothing or unnecessary pressure around the wound helps minimize pain. Regular check-ins with the healthcare provider keep discomfort under control and recovery on track.
Nutrition and Lifestyle for Faster Healing
A balanced protein, vitamin C, and zinc diet supports tissue repair. Staying hydrated improves blood flow and cell regeneration. Smoking and alcohol consumption delay recovery and should be avoided. Moderate exercise helps circulation, but a doctor must clear it. These simple lifestyle adjustments can make a visible difference in healing outcomes.
Professional Wound Care Importance
Professional wound care gives patients access to advanced technology and expert oversight. Clinics use evidence-based practices to clean, assess, and protect wounds at every stage. Patients receive personalized care plans tailored to their health conditions and recovery pace. According to 2024 clinical reviews, patients who receive specialist care heal nearly twice as fast as those managing wounds alone.
Signs That Require Specialist Attention
If a wound hasn’t improved after two weeks, it may need debridement. Dark, hardened tissue, persistent odor, or excessive drainage are warning indicators. Swelling, heat, or worsening pain also suggest deeper infection. Seeking professional care ensures these issues are treated before they progress. Trained specialists identify root causes that standard home care may overlook.
Long-Term Benefits of Specialized Treatment
Specialist care reduces infection risks, prevents recurrence, and promotes cleaner, more substantial healing. Patients benefit from ongoing evaluations and guidance on proper wound management at home. Clinics may also offer advanced and regenerative therapies, such as negative pressure wound therapy, platelet-rich plasma (PRP), and growth factor treatments, which stimulate tissue repair and speed recovery. These innovative options encourage new cell growth, improve circulation, and strengthen healing tissue. Personalized care plans built around these methods lead to faster recovery and lasting skin health. Continuous monitoring ensures that healing remains consistent, predictable, and complete.
Long-Term Healing and Recovery After Debridement
Healing extends beyond physical repair; it also affects confidence and emotional well-being. Staying patient during recovery can be challenging, especially for those with chronic wounds. Encouragement from healthcare teams and loved ones makes the process easier. Tracking progress helps patients appreciate each milestone as a victory.
Preventing Future Wound Problems
Protecting skin integrity reduces the chance of future wounds forming. Keeping the skin clean and moisturized helps prevent cracking or sores. People with diabetes or circulation issues should inspect their skin daily. Wearing proper footwear and avoiding friction-prone clothing adds another layer of protection. Regular medical checkups maintain wound-free health and sustained healing.
Emotional Support During Healing
Recovering from a wound can cause stress or frustration. Emotional support plays a vital role in maintaining motivation and optimism. Healthcare providers encourage open discussions about fears and expectations. Joining a support group or speaking with a counselor can help manage stress. Emotional well-being directly impacts how well and how quickly the body heals.
Find Lasting Relief Through Expert Wound Care Solutions
Wound care solutions go beyond covering an injury; they create the ideal environment for proper healing. Combining professional wound debridement with advanced dressings and antimicrobial treatments removes damaged tissue while supporting new, healthy cells. These products help maintain moisture balance, reduce infection risks, and promote faster, cleaner recovery. When paired with expert care, modern wound care solutions restore comfort, strengthen skin, and give patients the confidence to move forward with lasting healing.
Your healing journey deserves clarity and confidence. The Stem Health Plus LLC blog offers trusted wound care and recovery tips.
